Advice Blog
Shoulder Pain Relief: Exercises, Self-Care Tips & Treatments That Work
Shoulder pain is one of the most common issues people face, whether from work, sports, or poor posture. Because the shoulder joint is the most mobile in the body, it’s also more prone to injury and irritation. Left untreated, shoulder pain can interfere with sleep, workouts, and even simple daily tasks like reaching overhead or lifting objects.
The good news? With the right self-care strategies and professional treatment options, most shoulder pain can be managed and often resolved.
What Causes Shoulder Pain? Common Reasons Explained
Common causes include:
-
Overuse or repetitive strain from work, exercise, or sports.
-
Rotator cuff injuries (small tears or tendon irritation).
-
Tendonitis or bursitis (inflammation in tendons or bursae).
-
Arthritis or age-related wear and tear.
-
Posture-related pain, often from long hours at a desk or on a device.
Best Self-Care Tips for Shoulder Pain Relief
General Tips
-
Keep moving: Gentle, frequent movement is better than rest alone. Don’t push through sharp pain, but don’t let the shoulder “freeze up.”
-
Apply ice or heat: Ice helps reduce irritation in the first 48 hours; gentle heat can ease stiffness afterward.
-
Check your posture: Keep shoulders back and avoid prolonged hunching at your desk or phone.
Shoulder Pain Exercises Backed by Research
To reduce the risk of further injury to your shoulder we suggest consulting a professional to ensure these are safe and appropriate for you to do, as done incorrectly they could worsen your condition.
1. Modified Cross-Body Stretch

- Bring one arm across your chest.
-
Use the opposite hand to gently press the elbow toward your body.
-
Hold 30 seconds.
-
Repeat 3 times, 1–2x daily.
2. Sleeper Stretch

-
Lie on your side with the affected shoulder underneath.
-
Bend the elbow to 90°.
-
Use your other hand to gently press the forearm down toward the floor.
-
Hold 30 seconds.
-
Repeat 3 times, daily.
3. Wall Crawl

-
Stand facing a wall.
-
“Walk” your fingers up the wall as high as comfortable.
-
Slowly return to the start.
-
Repeat 5–10 times, 2–3x daily.
4. Resistance Band Scaption
-
Stand on a resistance band, holding ends in both hands.
-
Raise arms in a V-shape (slightly forward, thumbs up).
-
Lift only to shoulder height.
-
Do 2–3 sets of 10–12 reps, every other day.
5. Isometric Rotator Cuff Holds
-
Stand beside a wall with elbow bent at 90°.
-
Push the back of your hand (external rotation) or palm (internal rotation) into the wall without shrugging or moving your shoulder.
-
Hold 5–10 seconds.
-
Repeat 10 times, 2–3x per day.
These exercises target both mobility and strength, which research shows is more effective than stretching alone.
When Should You See a Chiropractor for Shoulder Pain?
See a provider if you experience:
-
Pain lasting more than 2–3 weeks.
-
Night pain that disturbs your sleep.
-
Weakness or loss of motion.
-
Swelling or sudden severe pain.
Early treatment can prevent long-term problems and speed recovery.
Effective Shoulder Pain Treatments: Shockwave Therapy, Sports Massage & Chiropractic Care
At our clinic, we offer a full range of treatments designed to address the root cause of shoulder pain:
-
Chiropractic Care: Restores alignment and reduces joint stress.
-
Shockwave Therapy: Stimulates healing in muscles and tendons, breaks down scar tissue, and improves circulation.
-
Sports Massage: Relieves muscle tension, improves mobility, and promotes faster recovery.
- Clinical Pilates: Helps correct functional issues, restore range of motion and strength
All treatments come combined with a personalized exercise plan.
How to Prevent Shoulder Pain and Keep Your Shoulders Healthy
-
Maintain good posture throughout the day.
-
Warm up before exercise or sports.
-
Strengthen upper back and shoulder muscles regularly.
-
Take breaks from repetitive tasks and desk work.
-
Avoid lifting heavy objects overhead without proper form.
Take the Next Step Toward Relief
Shoulder pain doesn’t have to slow you down. Whether it’s caused by posture, overuse, or injury, there are proven ways to heal and regain comfortable movement.
👉 Call us today to schedule an appointment or to ask for further information and find out if chiropractic care, shockwave therapy, sports massage, or Clinical Pilates is the right solution for you.
029206177100
Work Station Ergonomics
Ergonomics : Tips to help you at home!
With an increase in the number of people working from home we have seen a surge in problems related to our patients home setup.
Many people find themselves using a computer for a large part of the day, and during these difficult times it's happening even more so.
Incorrect workplace design and layout can contribute to work related injuries (such as repetitive strain injuries), whilst correct chair height, adequate equipment spacing, and good desk posture can help you stay comfortable.
Quick Top Tips
- Take short frequent breaks, we're built to move. Many working from home are missing the mini-breaks they had working in an office environment, less distance to the kettle!
- Set an alarm/timer every 30 minutes to remind you to change position and correct posture.
- Build postural stretches and exercises in to your daily routine.
- Mix up your tasks during the day to use different muscle groups.
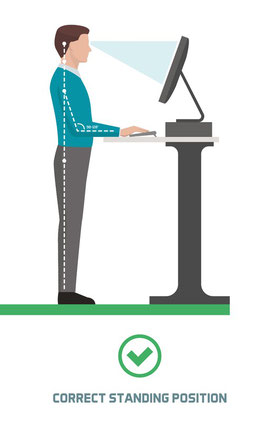
- Consider a standing desk to help vary the pressure on different parts of your body
- Those using laptops consider having a separate monitor or wireless mouse and keyboard so that you can position all well.
- Reduce screen time by listening to audio books or podcasts during your spare time, instead of watching TV or using phones.
- If you aren't able to access a computer chair remember to support your lower back with extra cushions.
- When choosing where to set up consider appropriate natural light, screen glare, and sight line. Ideally position somewhere you can occasionally look in to the distance to reduce eye strain (so not facing a wall or with sunlight directly behind you).
As home working seems likely to continue long term, more patients are considering investing in their own desks and office equipment. For our suggestions on how to set up your workstations, equipment ideas and more, please read on below.
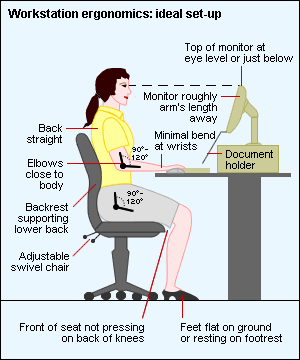
Desk
- Consider investing in a variable height desk to allow you to easily vary your posture without having to interrupt your work or meetings.
- Variable height desks allow for bespoke adjustments to suit your height, so can eliminate the need for footstools and ensure optimal positioning for you.
- Make sure you have plenty of space to work with so that you are not cramped (see document holder below).
Chair
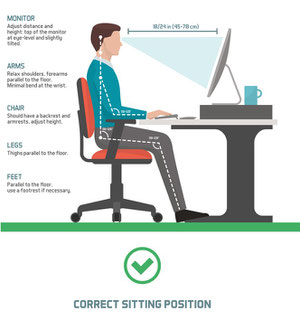
- Ideally, use a swivel chair with wheels or glides to allow easy chair movement.
- Adjust the height of your chair so that your feet rest comfortably on the floor or, if this makes your chair too low in relation to the desk, use a footrest.
- Your position when sitting, your knees should be about level with your hips, and the seat of your chair should not press into the back of your knees. Your spine should be against the back of the chair and your shoulders relaxed back and down.
- If your chair can’t be adjusted so that your back is straight, place a cushion between the curve of your lower back and the back of the chair.
Monitor

- Position the monitor should be roughly an arm’s length away. The top of the screen should be at eye level or just below so that you look down at a slight angle to your work.
- If you wear bifocals, position the monitor lower than normal to compensate for needing to look through the bottom of your lenses. Raise your chair until you can view the monitor without tilting your head back. This may mean that you have to raise the keyboard and use a footrest. Alternatively when working at the computer, use a pair of single-vision lenses with a focal length designed for computer work.
- Reduce glare and reflections, by ensuring neither you or the monitor face the window. Tilting the monitor slightly downwards can help with glare, and adjust the monitor’s brightness to a comfortable level.
- Remember to rest your eyes every 30 minutes or so, by looking away into the distance.
Keyboard

- Arm position should be such that you are able to have your forearms close to horizontal and your wrists straight when using the keyboard, and your elbows close to your body.
- Align with the monitor and directly in front of you, so that you don’t have to twist or rotate to use it.
- Put reference documents either between the monitor and the keyboard or directly alongside the screen in a document holder so the keyboard is not pushed too far back on the desk, disrupting your posture.
- The keyboard should not be so close to you that your wrists rest on the sharp edge of the desk.
Mouse

- Consider using an ergonomic mouse to better align you shoulder and reduce strain on your arm and neck.
- Position your elbow close to your body to help with arm and shoulder alignment and reduce strain.
- The mouse should fit the size of your hand so that it is comfortable to work with.
- Your wrist should be in a neutral position (minimal bend in any direction at the wrist) when you use the mouse, and your fingers should be able to rest on the push buttons between actions.
- If possible position the mouse on the desk so that the weight of your arm is supported by the desk.
Laptops and Tablets

Laptops were designed for short term or mobile use; however, this portability means that people often use them at an unsuitable work height and this may result in discomfort over a long period. There are several ways to address these problems such as
- Docking the laptop into a desktop computer at a suitable workstation.
- Connecting the laptop to stand-alone equipment such as a separate screen, keyboard and mouse.
- Transferring your information onto a desktop computer if working for long periods.
- Use on a desk where possible with a suitable chair.
- If on lap use a tray over a cushion to elevate the laptop, and the tray will insure the fans aren’t blocked.
Gardening
Gardening Tips for Low Back Pain Management

With the change of seasons, we find ourselves tackling our gardens ready for summer time.
Even though gardening is not considered as a sport it is very physical and time consuming, resulting in the body being in the same position for long periods of time.
Gardening involves a lot of forwarding bending and at times can result in us twisting ourselves into awkward positions.
These can result in spinal and surrounding structures to be strained and therefore resulting in back pain.
We have put together some helpful tips for you to incorporate into your gardening regime in order to prevent or manage any low back pain you may experience due to gardening.
Warm up First
It is a good idea to warm the muscles up first prior to gardening, as you would with any other type of work out. This could be a brisk 5 minute walk with or without some gentle stretching. Below is a few stretches that will help to loosen the low back ready for gardening.
If you already suffer with low back pain we would advise that you speak with your Chiropractor or healthcare practitioner in order for them to advise you on what stretches would be most appropriate for you.




Lifting Technique
Incorrect lifting technique is a common trigger for low back pain. Even more so when you have been gardening for a long period and make a sudden movement.
To lift correctly, begin by squatting and not bending the waist. Use both hands to hold object, keeping it close to your body and slowly straighten legs as you lift.
Try to limit the amount of lifting you do by either using lifting aids or asking someone to help.
Another tip would be to half your lifting load, such as putting half the soil into a bucket to carry or half the water in a watering can.

Take regular breaks
Be conscious to keep track on time and not stay in the same position. Get up and move around, try some light stretches and try out different positions.
Try to avoid carrying out the same job for a long period of time. Switch between jobs so that you are alternating your posture set ups.
Use support aids
Try to use support aids to make you feel more comfortable such as chairs or cushions. Getting up and down from positions esp up from the ground can be a difficult task so use aids to help you alter your height.

Use correct equipment
It is worth investing into the correct gardening equipment for your needs. As these will aid you and prevent you from over compensating in order to get the job down e.g long handed tools can help to eliminate bending.
Ask for help
Do not be afraid to ask family, friends, neighbors etc for help. If a task is is too much for one person or you are suffering with any discomfort as someone to help or take over. It is important to understand your own limitations.

If you are experiencing some pain following a gardening session then the following may be useful:
- PRICE (protection, rest, ice, compress and elevate).
- Find your pain free movements and try to avoid any painful movements.
- NSAIDS, over counter pain killers (always read label).
- Use support aids.
The above listed are not conclusive to the type of pain, and you may find that you do not fit into a particular area. Therefore it is important to seek professional health if you are experiencing pain.
See your Chiropractor if you are in pain
Chiropractors specialise in assessing, diagnosing and managing conditions of the spine. They are highly trained in finding the cause of pain in the spine. In the UK they undergo a minimum of four years’ full-time training. Importantly, chiropractors are regulated by law and must work within strict professional and ethical boundaries.
Before starting treatment, a chiropractor will do a full assessment. This will involve taking details about your condition, current health and medical history, and performing a physical examination. Sometimes it may be necessary to refer you for other tests, such as X-rays, MRI scans or blood tests. It is important for your chiropractor to gather as much information about your back pain as possible so that the most precise diagnosis can be made.
Your chiropractor will then explain what is wrong, what can be done and what you can expect from chiropractic treatment.
Chiropractors are best known for manual treatments such as spinal manipulation, where they use their hands to free stiff or restricted joints, or mobilisation, which is the gradual moving of joints.
But they may also use other recommended treatments such as certain types of acupuncture, electrotherapy, stretching exercises and rehabilitation, all of which form part of a chiropractor’s package of care. Your chiropractor may also offer lifestyle advice to help recovery and to prevent repeated episodes of back pain.
If your chiropractor does not think you can be helped by chiropractic treatment, you may be referred back to your GP or to another health professional. Chiropractors do not prescribe medication, so if this is needed, you may be referred back to your GP. As chiropractors support a joined-up approach to care, they may ask if they can send a brief report to your GP.
Many people who suffer long-term back pain benefit from regular, supportive chiropractic care to reduce the risk of recurrent episodes.
Avoiding Mishaps when Gardening

Gardening
Gardening – Don’t overdo it with the spade or trowel!
As a nation, we love our gardens and spend a considerable amount of time and money on them. As we rush to get those jobs in the garden done, there is a risk that gardeners may injure themselves. What everyone wants is to be fit and healthy enough to actually enjoy sitting in their garden and enjoy the fruits of their labours come summer time, so here are some helpful tips from the British Chiropractic Association.
Gardening
Gardening – Don’t overdo it with the trowel!
As a nation, we love our gardens and spend a considerable amount of time and money on them. As we rush to get those jobs in the garden done, there is a risk that gardeners may injure themselves. What everyone wants is to be fit and healthy enough to actually enjoy sitting in their garden and enjoy the fruits of their labours come summer time, so here are some helpful tips from the British Chiropractic Association.
Clothes
Don’t wear clothes that are tight or could constrict your movement.
Warm Up
Gardening is like any other exercise; you need to warm up first. Don’t go straight into heavy garden work; start off with lighter jobs as this will lessen the chance of muscle strain.
Using a ladder
· When using a ladder or steps, make sure you are always facing it, keeping your shoulders, hips and knees pointing in the same direction.
· Rather than leaning or reaching, move the ladder or step regularly to keep up with where you are
· Any kind of ladder must be firmly and safely planted in position and, if possible, have someone else there to keep an eye on things.
Clever pruning
· Get as close as possible to the things you are pruning and avoid overstretching to reach the area you are dealing with.
· Invest in some long handled secateurs to reach plants and bushes that are beyond normal reach.
Take a break
· Vary your activity by spending no more than 20-30 minutes on any one thing and make sure you take regular breaks. Be clever with the paving
· If laying a patio, keep the slab close to your body and bend your knees; it is sometimes better to bend one knee rather two, as your supporting leg gives you a position of strength.
· If using railway sleepers, two people will probably be needed.
Plan ahead
· If you are planning a trip to the local DIY store to buy heavy items such as cement or gravel, buy smaller bags rather than one big bag as they are easier and safer to carry.
· If you do buy heavy items, use a trolley and if on your own, ask an assistant at the store to help you. If buying things like compost, sand or gravel in bulkier amounts, shovel the contents of the large bags straight into smaller containers or wheelbarrow from the back of the car.
· Don’t lift with your arms straight out, keep the elbows bent and to your side to minimise the stress on your back.
· If having items delivered, have them unloaded as close to where you need them as possible; this will save the effort of moving them again.
· A specialist garden trolley might be worth investing in to move these sorts of materials around, especially if you have lots of patio pots to move around as well.
Courtesy of British Chiropractic Association
Buying a New Bed & Sleeping Position
Buying a New Bed

This month sees 'National Bed Month', and 14th March was 'World Sleep Day'.
Chiropractors are often asked for advice on the selection of beds and mattresses and, in truth, there is no one solution that suits all. Choosing the right bed can
minimise those factors that may lead to, or aggravate back pain. We come in different weights, shapes and sizes, but have one thing in common; we spend more than a third of our
lives in bed, so should choose our beds carefully.
Common Questions Answered:
Which is better, a hard or soft mattress?
- The best mattress is a ’supportive one‘. A 16 stone person sleeping on a mattress may not get the same support as a 10 stone person sleeping on the same mattress.
How do I know which is the right mattress for me?
- If you are lying on your side, your spine should be parallel to the mattress and your spine should not sag (bed too soft) or bow (bed too hard). The longer you can spend lying on a mattress before you buy it, the more accurate this feeling will be.
- Your pillow should be an extension of this i.e. your neck should be a continuation of the straight spine and not too high or too low.
What about my partner?
- Always shop with your partner as your respective ideal mattress tensions could be very different. If this is the case, buy beds from a range that allow two single mattresses to be zipped together, so that you both get the support you need.
How do I know if my current bed/mattress needs replacing?
- Are you and your partner getting comfortable nights sleep? If the answer is no, your bed may be the problem.
- Can you feel the springs through the mattress? If the answer is yes, it is definitely time to buy a new one.
- Is the bed more that 10 years old? If the answer is yes, consider purchasing a new one – beds wear out and may sag or lose support with time.
What things can I do to help prevent back problems even with my new mattress?
- Try and adopt a sleeping position which creates less physical stress on the back. For example, lying on your side is better than lying on your front with your neck twisted to one side.
- Keep moving and avoid being in any one position for too long. No matter how comfy the position may initially feel, the longer you stay in one position, the more this will ‘load joints’. If your partner moves around a lot at night, try separate beds for a while as your partner’s movement could aggravate YOUR back condition!
- Drink water. Keep well hydrated; dehydration can make muscles ache.
- Don’t leap out of bed first thing in the morning. After you have woken up wake up, try some gentle stretches.
- Wake up your body. Once up, avoid bending or doing anything sudden or strenuous until you back wakes up!
Bed advice UK provide impartial advice on how to choose the bed that's right for you: https://bedadvice.co.uk/bed-buyers-guide/buying-a-bed-thats-right-for-you/
Sleeping Positions

We all have our favourite sleeping positions, but some may be doing more harm than good. People who find it difficult to get comfortable don't have good quality sleep, as they are tossing and turning into weird and wonderful positions!
Patients often come to see me with pain they have woken up with, or they're not quite sure how it started through the day. Very often this is caused by the way they have slept. This image illustrates some of the most aggravating positions that we can sleep in (front being the worst), and some options if you have back pain to keep you comfortable.
REMEMBER DRINK PLENTY OF WATER - This helps us keep our muscles and joints hydrated and therefore pain to a minimum.
AVOID SLEEPING ON YOUR FRONT - A lot of front sleepers present to us in clinic with chronic problems as it’s difficult to maintain a neutral spine position. Sleeping on your stomach forces your head and spine into an unnatural position, and staying in this position for hours on end is not good for your back or neck and can result is significant discomfort and restless sleep. Patients have seen great results from trying to change their habits.
As I always say you can't control what you do in your sleep (especially snoring!) and it is hard to change the habit of a life time, but we can try and set up in a good sleeping position to avoid it.

This image shows how the spine and pelvis position can be distorted without the appropriate mattress support or positioning.
Sleeping with back pain

The key to sleeping well is to keep your spine as naturally aligned as possible. Whether you are a back sleeper or a side sleeper, understanding the alignment of the spine and maintaining that alignment while you sleep is a good starting point.
When side lying use a pillow between your legs to lift the top knee and take pressure off your hips and lower back.
*Some patients tell me they find it hard to keep a pillow in place so suggest trying a longer body pillow or small folded quilt. This is especially good for front sleepers who want to avoid rolling*
If on your back, a pillow positioned under your knees takes pressure off your psoas muscles which allows your back to flatten and relax. This can be put under the bed sheet to avoid loosing it in the night!
Front sleeping can cause your lower back to curve more, particularly if you have a soft mattress, and your neck will have to rotate. If you can't avoid it, use a thin pillow under the abdomen to elevate, and try sleeping without any pillow under your head
For more detail on the pros and cons of different sleeping positions check out this article by the Sleep Foundation: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/sleeping-positions
Pillows
These illustrations demonstrate how an incorrectly placed pillow can stress the neck.
On your back you need fewer pillows than on your side so if you change from on position to another bare this in mind. We are also all different shapes so the amount of support we need varies from person to person.
If you're a back sleeper I recommend using one pillow, thickness depends on the depth of your natural curves, and pull the lower corners around your lower neck so the pillow is no lower than your shoulders.
For side sleepers, or those who tend to end up in this position, you need plenty of support so try two pillows, again the depth required depends on the width of your shoulders. Ensure you are not at the edge of the pillow and the lower front corner is pulled down to your shoulder and around the cheek. This will prevent you head dropping or rotating which can irritate the neck or lead people to sleep on their front.

Avoiding Injuries When Running

A new year is here and with it, for many comes the desire to get back to fitness routines and don a pair of trainers to hit the road for a run.
Here’s how not to make it a troublesome one for your joints and muscles…
When running for longer than usual and pushing your body that little bit more it might result in unwanted injuries. You
should always listen to your body’ natural resistance and follow these tips for a safe and effective wind down after your run:
Don’t Stop Moving
Keep gently mobile right after your run. Try regular walking for 5-10 minutes; it might be the last thing you feel like after running a few miles but remaining static should be avoided at all
costs to avoid injuries.
Ice
Applying ice to specific injuries such as problems with joints is highly recommended. This is most effective when the ice is applied immediately after a run but still works when applied a few
days following.
Heat
Taking a hot bath after a long run is ideal for strained muscles. It also helps with overall rejuvenation and relaxation, which is often needed after a strenuous or draining stretch.
Food For Thought
What we put in our bodies pre and post run is particularly important. Snack regularly, ideally on something that is high in carbohydrates, low in fat, which contains some protein; for example, a
tuna sandwich is ideal. Ensuring you drink lots of fluids is also another very important factor for runners to remember. Water is of course an excellent choice when it comes to keeping well
hydrated but there are plenty of other options out there, too, such as sports drinks and gels. Remember: after finishing your run, rehydrate as soon as possible, preferably within the first hour
and always refrain from drinking alcohol until fully rehydrated.
Leg Pain in Running & Sports

With the growing popularity of community-based races and charity half marathons, more and more people are taking up running for fun. While running is associated with a lot of health and general wellness benefits, some athletes experience overuse injuries while running and training. One of these is exercise-related leg pain (ERLP), otherwise known as shin splints, with pain between the knee and ankle during or after exercise.
M Reinking, T Austin, and A Hayes (2013) looked into the prevalence of ERLP in adult runners and how the pain affected their running and daily activities. They also analysed risk factors to determine who is most likely to have leg pain from running. Out of over 200 runners, more than 50% of the runners reported at least one episode in the past year. Of this group, about 40% said that the leg pain interfered with running. They found that the most significant risk factor was previous leg injury or pain and participants who had less than three years experience running were at greater risk than more experienced runners. Those who ran less than 15 miles per week were more likely to suffer leg pain than those running more. The greatest occurrence was among amateur runners who raced at a pace of 9 minutes per mile or greater.
Some Causes of Leg Pain in Sport
Trigger Points

A trigger point is a hypersensitive, nodal point of muscle that can refer pain in specific patterns (Travell and Simon's Myofascial Pain and Dysfunction Vols 1 & 2) depending on if they are active or latent. Trigger points can build up due to an acute overload/injury, or chroinic overload such as repetative strain injuries.

This can be caused by a change in technique, increased training, or faulty mechanics in a joint or muscle (scar tissue etc). Trigger points weaken and shorten the muscle, effecting both strength and endurance. This in turn leads to further dysfunction in the surrounding tissues and joints as they compensate and are over loaded. Further trigger points then form in a snowball effect.
Snapping Hip Syndrome

‘Snapping hip’ or coxa saltans/iliopsoas tendinitis/dancer's hip describes an audible snapping or popping noise as the hip moves from flexion (knee toward waist) to extension (knee down and hip joint straightened). After extended exercise pain or discomfort may be present caused by inflammation of the iliopsoas bursae. Pain often decreases with rest and diminished activity.
The more common lateral extra-articular type of snapping hip syndrome occurs when the iliotibial band, tensor fascia lata, or gluteus medius tendon slides back and forth across the greater trochanter.

Less commonly seen medial extra-articular type is caused by the iliopsoas tendon catching on the anterior inferior iliac spine(AIIS), the lesser trochanter, or the iliopectineal ridge during hip extension, as the tendon moves from an anterior lateral (front, side) to a posterior medial (back, middle) position.
‘Snapping Hip’ syndrome is commonly associated with a leg length difference (usually the long side is symptomatic), tightness in the iliotibial band(ITB) on the involved side, weakness in hip abductors and external rotators, poor lumbopelvic stability and abnormal foot mechanics (Overpronation). Intra-articular can also be indicative of injury such as a torn acetabular labrum, recurrent hip subluxation, ligamentum teres tears, loose bodies, articular cartilage damage, or synovial chondromatosis (cartilage formations in the synovial membrane of the joint).
Stress Fracture
The more rapid the onset and the more acute the onset, the more likely it is that this could represent a stress fracture. Stress fractures are subtle fractures that occur in the bone as a result of putting too much constant stress on the bone, to the point where the bone starts to break — initially at a microscopic level. Stress fractures are common in athletes or runners who have changed their training schedules, increased the amount of time that they are playing or running… or simply bad luck. The pain from a stress fracture will typically be present from the first step you take on the court or the road.
Compartment Syndrome

A compartment syndrome is characterised by having too much pressure in the muscle compartments in our leg. Our muscles are surrounded by very tough tissue we call fascia, it is not very flexible and some runners or athletes experience muscle swelling during activities. If this swelling is significant enough, the fascia will squeeze or put pressure on the muscle. This reduces blood flow to the muscle and the muscle will fatigue rapidly and start to hurt. People with compartment syndromes typically have no pain at the start of their run/game, but at some point during the run/game pain will start and steadily build. You will typically need to stop your activity to relieve the pain. Sometimes compartment syndrome can become so chronic and severe that it requires surgery to reduce the pressure, so best to get it looked at by chiropractor as soon as possible for prevention.
Shin Splints
The pain from shin splints or medial tibial stress syndrome tends to build gradually and is a form of compartment syndrome. You can usually initiate a run, or a game and then the pain begins shortly thereafter, or possible after the game or run itself. Medial tibial stress syndrome (or ‘shin splints’) is characterised by pain along the lower part of your leg or tibia, and the pain is along the inner border of the tibia. This is a very common cause of disability in runners and they often develop after sudden changes in physical activity, such as running longer distances or on hills, or increasing the number of days you exercise each week. Flat feet (weak arches) are another factor that can contribute to increased stress on the lower leg muscles during exercising.
Tendonitis

Tendonitis (tendon inflammation), or Tendinosis (degeneration of the tendon) is a very common issue sports medicine specialists see in sports and runners. One of the most commonly affected tendons is the achilles. If the tendon, a few inches above your ankle joint is tender, but you do not feel or see any nodules you are most likely suffering from a form of tendonitis or peri-tendonitis where the tendon itself, or the tissue around it is inflamed from chronic use. Achilles tendinosis is caused by a chronic tendonitis, causing nodules or enlargement of your tendon that is tender to touch, diagnostic ultrasound can confirm the diagnosis. Chronic achilles tendinosis causes scar tissue and weakening of the tendon, which can potentially lead to rupture.
Treatment
Chiropractic care, Shockwave Therapy, and Sports Massage have been shown to be a great option for athletes in both treating and preventing sports injuries and pain. One such study found that chiropractic treatments led to less muscle strains in the legs. Another study showed that chiropractic adjustments improved athletic performance among competitive athletes (references below). Through soft tissue techniques and spinal manipulation, combined with advice, we can work to prevent injury occurrence.
References
Botelho, Marcelo and Bruno Andrade. “Effect of Cervical Spine Manipulative Therapy on Judo Athletes’ Grip Strength. Journal of Manipulative and Physiological Therapies. 2011; 35(11): 38-44.
Hoskins W, Pollard H. The effect of a sports chiropractic manual therapy intervention on the prevention of back pain, hamstring and lower limb injuries in semi-elite Australian Rules footballers: a randomized control trial. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2010;11:64.
Reinking M, Austin T, Hayes A. A survey of exercise-related leg pain in community runners. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy 2013; 8(3): 269-276.
Sciatica

Sciatica is a commonly used term to refer to that sharp shooting pain down the back of your leg. It is, however, a symptom of an underlying cause, not a diagnosis itself. In this post we will explore some of the different possible causes of this uncomfortable symptom..
Many causes for sciatica are nothing to be concerned about and can be treated and generally ease with time, despite being uncomfortable and often painful. However, in some cases the cause for sciatica can be more sinister and require attention immediately.
If you’re experiencing sciatica in both legs, have a weakness or numbness in both legs that is progressing, have numbness in the saddle area (genitals), bowel and bladder changes, seek medical attention immediately.
Disc herniation

A common cause of sciatic nerve compression is when discs between the spinal vertebra herniate. In many cases this won’t interfere with the nerve roots exiting the spinal canal, and they may result in just lower back pain or be asymptomatic. However, If a herniated disc pushes onto a nearby nerve root, you will likely experience some nerve pain that will follow the path of this nerve. If this is in the low back, the pain commonly refers down the back of the leg via the sciatic nerve (S1).
Disc herniations are most common in the bottom few spinal levels, so can also affect other nerve roots which will cause leg pain in different locations. This allows us to diagnose which levels might be affected, alongside neurological testing of reflexes, sensation & muscle strength.
Spinal stenosis

The central canal of the spine can become narrowed and put pressure on the spinal cord, often seen in older age groups where the spine is more prone to degenerative changes. Often lumbar spinal stenosis is asymptomatic, but it can result in irritation of the sciatic nerve and cause leg pain too!
In these cases leg pain is often worse with back extension, prolonged standing and walking. Often progressing in its' intensity until you rest or bend forward. It is also called neurogenic claudication.
Symptoms are typically in both legs accompanied by lower back pain, with numbness and tingling present in the majority of patients.
Piriformis Syndrome

The piriformis muscle runs from the bottom of your spine (sacrum) to your hip crossing the path of the sciatic nerve. In some people the sciatic nerve runs through this muscle, and in these cases, the sciatic nerve may be more prone to irritation.
If the piriformis muscle becomes overused, irritated or inflamed, it can compress the nearby nerve resulting in sciatic nerve irritation and the leg pain you may be experiencing. Typically patients experience:
- Chronic pain in the buttock and hip area
- Pain when getting out of bed
- Inability to sit for a prolonged time
- Pain in the buttocks that is worsened by hip movements
Sciatica Treatment

The good news is chiropractic care may be able to help. Sciatic pain and its causes are conditions that chiropractors are trained to treat and see regularly in clinic.
During a chiropractic consultation we will take a detailed case history, conduct a thorough physical and neurological exam to localise the cause of your pain. We will then work together to create a personalised treatment and rehabilitation plan. If needed we can also organise a referral for imaging or another appropriate care provider if chiropractic isn’t suitable for you at this time.
The classic chiropractic spinal manipulation is not always an appropriate treatment for our patients, especially those with acute disc prolapses. Below are some different techniques that our chiropractors might use to help you with your sciatica symptoms.
Flexion-Distraction

Flexion-distraction is a form of traction that gently mobilises and stretches your spine, gaping your vertebrae and opening up the spaces where the nerves are getting compressed.
As well as stenosis and disc herniations, flexion-distraction can be used to treat many other causes of lower back pain. It can reduce pain and stiffness associated with osteoarthritis and can be helpful if you have sacroiliac syndrome, ankylosing spondylitis, sprains, and strains. It's also very effective in treating muscle spasms or low back pain unrelated to a specific condition. The technique is gentle enough to use after spinal surgery and can be a safe therapy option for those who have osteoporosis.
In a study published in The Journal of Physical Therapy Science, researchers examined the effects of flexion-distraction manipulation on patients with lumbar spinal stenosis. Study participants who received flexion-distraction manipulation as part of their treatment experienced a greater reduction of their painful symptoms than those patients whose treatment did not include the technique.
NCBI: Journal of Physical Therapy Science: Effects of Flexion-Distraction Manipulation Therapy on Pain and Disability in Patients with Lumbar Spinal Stenosis, 30/6/15
Acupuncture/Dry needling

Acupuncture stimulates the nerves in skin and muscle, producing a variety of effects. It increases the body's release of natural painkillers, endorphins and serotonin, in the pain pathways of both the spinal cord and the brain. This modifies the way that pain is felt.
Modern research shows that acupuncture can affect most of the body's systems including; the nervous system and muscle tone.
This can be a useful tool to help patients struggling with neurological pain, and to relax muscle spasms.
Information obtained from the British Medical Acupuncture Society, cited 02/06/14
http://www.medical-acupuncture.co.uk/Default.aspx?tabid=79
To find out more about your sciatic pain and whether chiropractic treatment could help, book an appointment today.
4 Exercises for a Healthy Life
Exercise has benefits for nearly everybody. It is effective both as a treatment and for prevention of disease. Here’s four ways you can help yourself by getting moving!
Dancing Against Dementia

It’s thought that remembering steps and making split-second adjustments to your movements stimulates the brain’s ability to make new connections between cells. Music itself is believed to have a therapeutic effect, and the social interaction involved in dancing helps boost mental health.
Regular dancing is linked to a 76% reduction in the likelihood of developing dementia, according to US researchers, who studied the link between leisure activities and dementia risk.[1]
Dancing is also beneficial for dementia patients. A New Zealand study found that older adults with dementia appeared to have experienced an improved quality of life after exposure to music and dance. [2]
It doesn’t matter which step you do, so choose a dance type you enjoy, whether that’s waltz, salsa or something else. There are other proven mental health benefits of dance, including a reduced risk of depression and anxiety. Dancing also can affect your mood by raising levels of our natural feel-good hormones, dopamine and serotonin.
[1] https://blogs.biomedcentral.com/bmcseriesblog/2016/04/04/keep-dancing-turns-good-brain/
[2] https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2019/08/190808091401.htm
Cycling for Immunity

Cycling can hold back the effects of ageing and rejuvenate the immune system, a study has found.[1]
Scientists at the University of Birmingham found cyclists aged 54-79 produced more immune cells (T-cells), the production of which usually starts to shrink from your 20s. They also preserved muscle mass and strength with age while maintaining stable levels of body fat and cholesterol.
You can integrate it into your lifestyle, simply as part of your movement pattern. Regular moderate exercise is more beneficial than one big weekly workout, so it makes physical and economic sense to incorporate your bike ride into your everyday exercise.
[1] https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2018/mar/08/cycling-keeps-your-immune-system-young-study-finds
Walking for Insomnia

A study has shown that moderately intense aerobic exercise, such as walking, reduces the time it takes you to nod off and increases the duration of sleep.[1]
It could in part be due to the release of anxiety-busting brain chemicals such as serotonin, and the rise and subsequent fall in body temperature that helps promote sleep. Walking outside in natural daylight also helps to set your circadian biological clock – your natural sleep-wake cycle, which controls the release of the sleepy hormone melatonin. And it’s not just great for a good night’s sleep. Walking helps to protect against cardiovascular diseases, cancer, bone-thinning osteoporosis, and dementia. It’s also good for our mental health to get outside and see gardens or green spaces, and walking can be sociable too.
[1] https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5093382/
Tennis for Osteoporosis

Regular weight-bearing activity, such as racquet sports, can help maintain bone density. Bone is a living tissue, which grows stronger with the force of our muscles pulling against it. Exercise can help delay the rate of age-related bone density loss. Osteoporosis is a condition where bone density and quality are reduced, and it affects more than two million women in the UK. After the menopause, when the protective effect of oestrogen on the bone is removed, there is often an accelerated rate of bone loss[1]. So playing tennis in later life is a great way to keep bones healthy. Another great reason to play tennis is that it can add 10 years to your life! It’s thought the social side of the game as well as the physical activity boosts longevity.[2]
[1] https://theros.org.uk/information-and-support/bone-health/exercise-for-bones/
[2] https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30193744/
EXERCISE - THE NEW PRESCRIPTION
'New Year-New You', something a lot of us promise ourselves. There are so many benefits to exercise, whether it's starting by going for a walk or enhancing an existing programme. Read on for many of the benefits you may not have thought of.
Of course with anything new there is always the risk of injury, so read below for the BCA's top tips to avoid injury.
Tim Hutchful, British Chiropractic Association (BCA) chiropractor, comments:
“It’s great to have the will and motivation to get fitter but bear in mind that exercise puts added pressure on our joints and muscles which could cause issues for your back and neck if not
introduced to your body in a safe way.”
So how can you prevent these injuries? The British Chiropractic Association has given the following advice:
It’s All in the Prep
• Before you begin any exercise programme check there are no medical reasons why you cannot commence the activity, particularly if you are not normally physically active.
Consult your GP if in doubt.
• A BCA chiropractor can advise you on how to approach a new exercise routine and tell you what signs to look for if you’re overdoing it.
• Make sure you get the right attire for your chosen activity; clothes that are too tight or inappropriate could constrict your movement leading to injury.
• Have appropriate footwear for the type of exercise you are doing – most specialist sportswear retailers will be able to guide you on this.
• With all exercise, you need to warm up first. Don’t go straight into it, start with lighter movements like walking or jogging to lessen the chance of muscle strain.
1. For Living Longer – Jogging
A US study showed that adults over 65 who ran or jogged for at least 30 minutes 3 times per week were as healthy as young adults in their 20s.[1] This might not sound important, but your walking style is a key indicator of mortality, so the longer you can stay spritely on your feet, the longer and healthier your life should be. Meanwhile, another study found that light jogging (between 70-120 minutes per week) was linked to the lowest mortality rate compared to sedentary people and heavy runners - so little and often is key here. [2]

2: For Improving Memory – Dancing
A study from 2017 found that all exercise can help reverse the signs of ageing in the brain, but dancing more than any other sport.[1] The
study, which focused on adults in their late 60s who took part in a weekly dance class, found that all participants showed an increase in the hippocampus region of the brain, which can be
affected by diseases such as Alzheimer’s and dementia, as well as more general age-related decline.
https://www.newswise.com/articles/new-study-jogging-keeps-you-young

3. For Back Pain – Active Therapies
Many GP appointments are connected to muscle and nerve problems- and these are often based in the back. If you suffer with back pain, you will know that it can affect your movement and sleep and leave you feeling quite low. Luckily, help is at hand in the form of gentle stretching. Also, research shows that active therapies, such as chiropractic treatment, are a great option for managing back pain and to create optimal alignment, balance and symmetry.

4. For Depression and Anxiety - Walking
Science agrees - walking outdoors has been linked to a reduction in stress and a boost in mood, particularly for those who have just been through a negative life event such as a serious illness or the loss of a loved one. Brisk walks have also been shown to help women deal with anxiety and stress that's sometimes associated with menopause. Movement helps your brain to release endorphins, the feel-good hormones that can reduce the perception of [pain as well as depression and anxiety.

5. For Bone and Muscle Health – Weight Training
Experts are increasingly suggesting a bit of strength training goes a long way when it comes to better bone and muscle health. As we get older, we start to lose muscle mass, which can leave us prone to falls, as well as making it easier to gain weight. So think of strength training as insurance for your later life. While this could mean leading to lift lightweights, it can also mean strength exercises using your own body weight – such as sit-ups or squats. It’s really never too late to start. A study of 90-year-olds found that 12 weeks of strength training improved their muscle tone, ability to balance, general power and walking speed.
Don’t forget 150 minutes (just over 21 mins daily) is the minimum moderate exercise the NHS recommends for adults to stay healthy! And the best part is, it’s freely available to most of us, small things make a big difference. Movement is the new medicine!
The Perils of Parenting

The British Chiropractic Association (BCA) are encouraging parents to straighten out their approach to back care as consumer research shows that 79%* of the UK population has suffered from back / neck pain at some point in their lives – 61%* of those being parents.
The research also shows that over half (55%*) of parents’ back or neck pain has prevented them from lifting or carrying their child. 40%* of
women said their back or neck pain had prevented them from carrying their child’s car seat or carry basket and 40%* of men said that back or neck pain had prevented
them from playing with their child.
How to care for your back when parenting

Choosing a cot:
- Find a cot which has sides that drop down to several levels, and a base that moves up and down. The less you have to lift and lean over to put your child into the cot, the better. A 'next to me' crib can ensure safe co-sleeping.
- A 5kg weight at your chest equates to five times that amount at arms length! So when placing your child in the cot, keep them as close as possible to you. Remember, you will be doing this thousands of times!
- Fix the cot to the floor or wall as toddlers can rock the cot causing it to tip, and either injure your child or you as you run to stop it falling.

Feeding:
- Whether breast or bottle feeding, find a comfortable posture. Your arms should not be bearing the baby’s weight, so use pillows to support your arms and shoulders.
- It is not uncommon for mums and dads to get neck strain from checking that the baby is feeding properly. Keep looking up to give the neck a rest, or if it is really painful try using a mirror positioned so you can see.
- When looking down tuck your chin in to engage the core muscles of your neck.
- Alternating feeding sides is a good idea when bottle feeding, as it evenly spreads any strain.
- Feeding a child in a high chair can place strain on your back. Sit as close as possible in front of your child and adjust the height of the chair so that you are not leaning too high or too low.

- Try different positions to best see which suits you and baby, and remember that will change as baby grows so keep experimenting.
- If baby is struggling to latch initially when breast feeding your flow might be too fast so try reclining slightly or reassess babies latch is correct.
- Try different formulas to see which suits baby best
- If baby struggles with wind and colic and there is a family history of IBS, dairy or gluten intolerance, speak to your midwife or health visitor about specialised formula milk. If breast feeding consider excluding these from your diet to see if symptoms improve.
- Ask your midwife or health visitor for advice as there might be local free groups you can join to help with positioning. In Cardiff contact the NHS Seren team who have weekly drop in clinics for weighing and positioning tips.
Prams/Pushchairs:
- A pushchair or pram with adjustable height settings is ideal, as it can be moved to suit your own height, and that of anyone else who will be pushing it.
- You should be able to walk upright with a straight spine and hands resting at a comfortable height.
- A pram or pushchair must be one that is easy for you to put up and collapse. Try them out to check! You don’t want the mechanism to be too stiff or complicated to work or require you to press down hard with one foot at the back, as this is not good for your back.
- Check you can safely carry it once collapsed; some people find that the shape a pushchair collapses down to is in itself, difficult to manoeuvre!
Carrying babies:
- Carrying your baby as close as possible to your centre of gravity, across your back or front is best.
- A carrier/sling or papoose is a good option. Select a carrier that ‘criss-crosses’ at the back, so baby’s weight is distributed more evenly, as opposed to across one shoulder.
- If carrying your baby without a sling or carrier or using one that is one sided, keep the baby’s weight close to your body and to your hip, with your spine straight, Swap sides regularly.
Carrying toddlers:
- For carrying a long way, a backpack carrier is best as it distributes the weight evenly across your back. Make sure you have the shoulder straps firmly tightened and click the waist strap into place. There are carriers that take the weight onto the hips, but make sure you use them with your spine straight.
- Encouraging toddlers to do as much as possible for themselves as appropriate, such as getting into the car seat, will save your back a lot of stress!
In the car:
- When putting your baby into the car, hold the baby close to you as you move towards the vehicle. Keep your back straight and only bend your knees when you have got as close to the car seat as possible. Only at this stage should you reach out to put the baby in the seat.
- If you’re carrying the baby in a chair, rest the chair on the edge of the car seat before bending to manoeuvre it into position within the car, keeping your knees bent and back straight.
- Don’t try to reach out too early and avoid bending from the waist by using your knees and hips.
Playing:
- Get down to your child’s level, rather than bending over. If sitting on the floor to play with your baby/toddler, try sitting on a cushion to help support your back and keep your back straight.
- Avoid spending too long kneeling down as this can put pressure on the knees. If you are kneeling, keep your back straight.
- Change position regularly.
- Don’t bend to pick up toys, bend your knees. Watch your child and observe the natural squatting posture they use to pick things up!
General Posture Advice:
- The fitter you are and the more muscle tone you have the less likely you are to injure yourself. Talk to your chiropractor, GP or other healthcare provider for advice on exercises to develop your core strength.
- Use a rucksack style bag is best as you can spread the weight evenly across your back. Check the straps are tightened so that the load is held against your back.
- Avoid high heels and wear comfortable, supportive shoes. If you have children already, it can be difficult if they need lifting and carrying.
- Always lift with your spine straight and bend knees to avoid leaning, stretching or bending. Simple activities such as stretching and shoulder shrugging can all help to keep your back in line.
- Do not sit for prolonged periods, take a regular break and, when sitting, let the seat take your weight and, if possible, keep as much of your body in contact with the chair so that your whole body is supported. Knees should be lower than your hips.